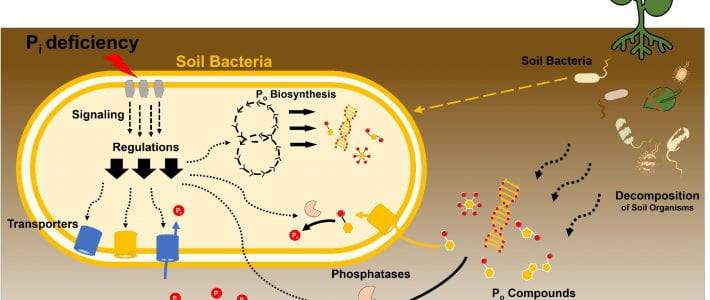
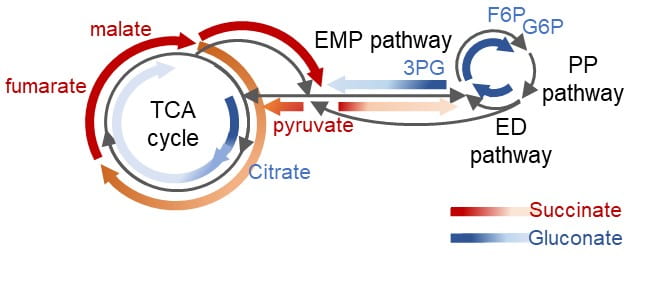
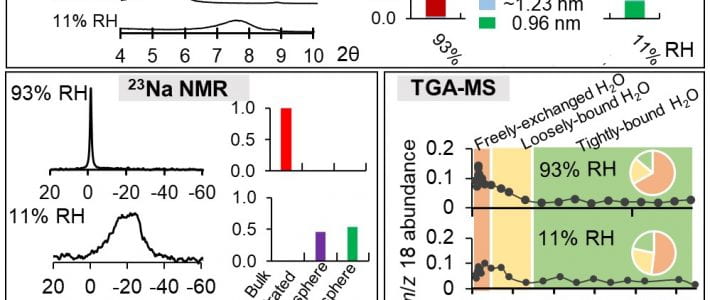
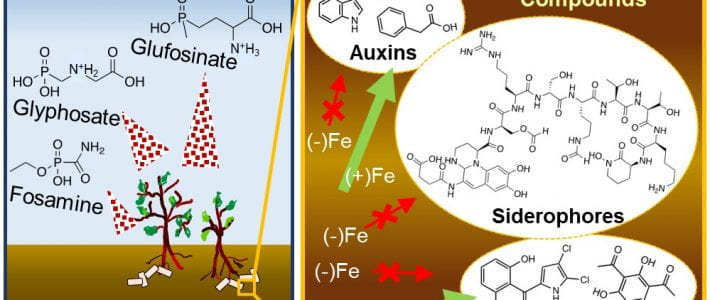
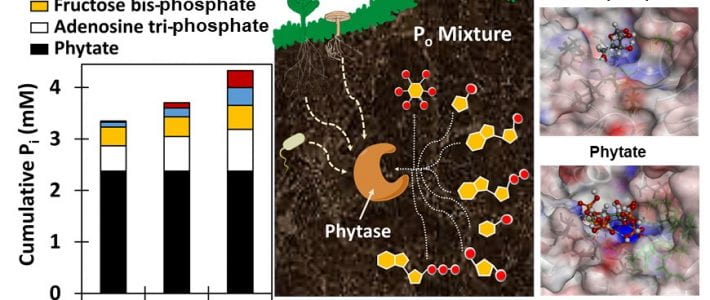
New article in Environmental Microbiology Reports by Park, Solhtalab, Thongsomboon, and Aristilde
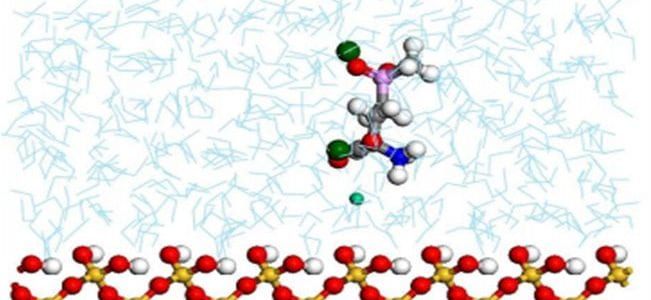
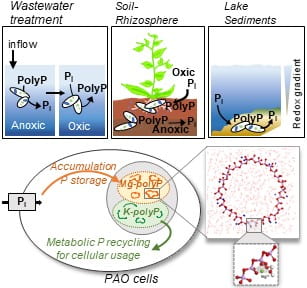
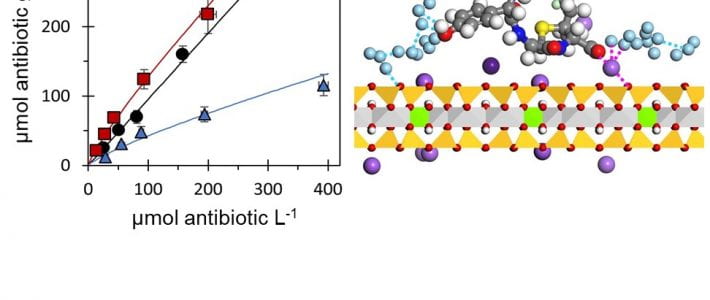
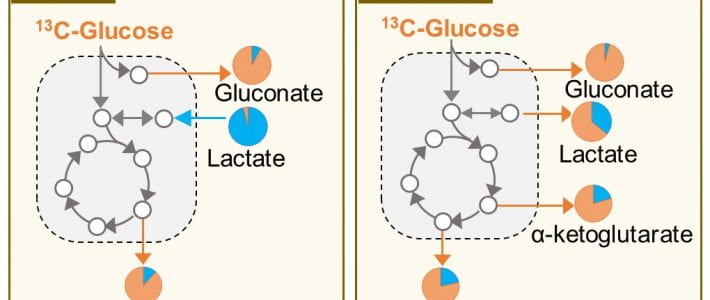
TITLE: Strategies of organic phosphorus recycling by soil bacteria: Acquisition, metabolism, and regulation –ABSTRACT: Critical to meeting cellular phosphorus (P) demand, soil bacteria deploy a number of strategies to overcome limitation in inorganic P (Pi) in soils. As a significant