TITLE: Evolution of Oxygen Isotopologues in Phosphate and Pyrophosphate during Enzyme-Catalyzed Isotopic Exchange Reactions
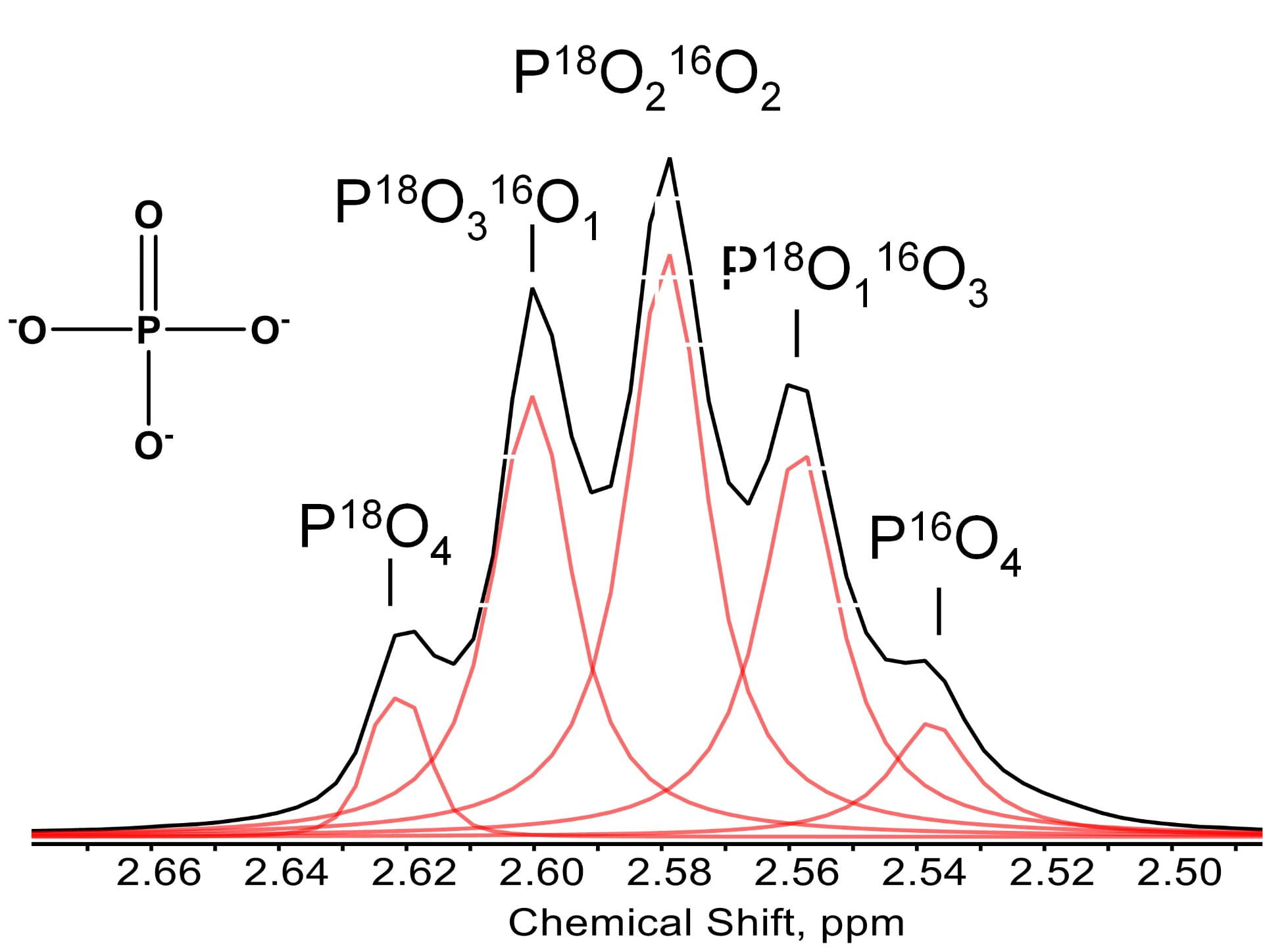
–ABSTRACT: Inorganic pyrophosphatase (PPase) is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of the phosphoanhydride bond in pyrophosphate (PPi) to release inorganic phosphate (Pi) and simultaneously exchange oxygen isotopes between Pi and water. Here, we quantified the exchange kinetics of oxygen isotopes between five Pi isotopologues (P18O4, P18O316O, P18O216O2, P18O16O3, and P16O4) and water using Raman spectroscopy and 31P nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) during the PPase-catalyzed 18O–16O isotope exchange reaction in Pi-water and PPi-water systems. At a high PPi concentration (300 mM), hydrolysis of PPi by PPase was predominant, and only a small fraction of PPi (≪1%) took part in the reversible hydrolysis–condensation reaction (PPi ↔ Pi), leading to the oxygen isotope exchange between Pi and water. We demonstrated that Raman and NMR methods can be equally applied for monitoring the kinetics of the oxygen exchange between the Pi isotopologue and water. It was found that the isotope exchange determined by the spectroscopic methods was detectable as low as 0.2% 18O abundance, but the reliability below 1% was much lower. Given that high P concentrations (≥1 mM) are required in these methods, environmental application of these methods is limited to rare high P conditions in engineered and agricultural environments. [Link to Article]